About thermoelectric module's failure
Reliability and product life is decided by solder connection.
|
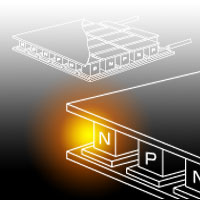
Thermoelectric cooler (module) is constructed of numbers of P-type and N-type thermoelectric chip and soldered together with cooper electrode formed on ceramic.
The number of soldering connection of thermoelectric cooler (module), in case of mostly used 127 pairs module, is 508 points. If included lead wire portion, there are 510 points of soldering connection. Because the electrical circuit is in series, 1 point of 510 solder connection's life will decide a whole thermoelectric module's life.
|
|
 |
Typical failure reasons
Depending on use conditions for application, failure reasons of thermoelectric cooler (module) are different. Typical failure reasons are in the following table. Please refer the detail description of each failure reason.
•
Typical failure reasons and solutions
|
Failure
Reason
|
Phenomenon
|
Happening
Condition
|
Solution
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thermal
cycle
fatigue
|
Cracks happen and get intensively on the connection of thermoelectric chip and cooper electrode, or on the thermoelectric chip itself, and finally, burn out and not able to be operated by electricity.
|
Temperature difference (ΔT) at operation is large or the machine with high thermal cycle frequency.
|
GL
structure
|
|
Corrosion
|
Cooper electrode connection solder, lead wire, or solder, etc. become eroded and cannot be operated by electricity.
|
Machine with the structure can be penetrated by humidity like condensation water, etc.
|
Humidity
protection
sealing
|
|
Migration
(short ~
breaking
of wire)
|
While condensation condition, solder between thermoelectric chip and cooper electrode is causing migration with cooper electrode, and gradually internal resistance is going down and turns into no cooling ability finally.
|
Machine with the structure can be penetrated by humidity like condensation water, etc.
|
Humidity
protection
sealing
|
|
Crystal
defect of
thermoelectric
element
|
In case of inclined cleavage plane of thermoelectric element it may lead to burning out of TE element due to concentrated joule heat.
|
If exists TE element which includes inclined cleavage plane.
|
Carry out
QC fully
|
■
About thermal cycle fatigue
This is the most typical failure of thermoelectric cooler (module), which happens naturally on the solder connection between thermoelectric chip and cooper electrode or around thermoelectric chip itself. Because thermoelectric cooler is the device utilizing temperature difference (ΔT) between heat absorption (low temperature side) and heat dissipation (high temperature side), so it generate thermal stress naturally. The largest thermal stress is located on thermoelectric element or junction at the corner of thermoelectric cooler (module), which starts causing cracks from thermal cycle fatigue and gets intensive slowly. Along with crack develops, crack surface will be oxidized, then the resistance of that portion will go up, and due to the increasing joule heat, the partial temperature goes up, finally burn out or solder and thermoelectric element melted to cause the breaking of wire.
■
About corrosion
It will certainly cause dew formation in case the machine needed to be controlled at lower temperature than room temperature. This dew water stays in the thermoelectric cooler (module), and corrosion will happen on solder part first. Since the solder connecting part contacts with different metal and solder include base metals, and it will be corroded firstly. If the corrosion gets intensive, cooper electrode will be corroded as well. Finally, no matter which case happened, the circuit will be cut off to end its life.
■
About Migration (short ~ breaking of wire)
Same as corrosion, this happens under the use condition of dew formation. When the dew water is in series with electrodes, the solder component elutes and moves due to the difference in potential existed between electrodes and metallic ion density will increase, then precipitation will form on the ceramics. The short circuit will caused by this repeating elution movement and precipitation. As a result, the internal resistance of thermoelectric cooler (module) decreases gradually, then cooling ability decreases as well. The solder connecting section area between thermoelectric element and electrode will become smaller, so that electrical resistance and joule heat will both go up, then finally burn out or connecting part is melted and cause the breaking of wire to end its life.
■
Crystal failure of thermoelectric element
In case the cleaved surface along direction of crystal formation of thermoelectric element is inclined largely, once chip is cleaved by thermal stress or mechanical strength, separation will be caused on elements by relationship of geometric position and electrode, which will get some sparks between cleaved surfaces, might be melted partially and disconnection might happen due to increased joule heat.